acetabular labral tear tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology : importing A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question. It defines an autoclave and describes its key components like the pressure chamber and lid. It explains how autoclaves work by using steam heat to kill microbes at temperatures above 100°C. The document outlines the .The purpose of this document is to provide standard operating procedures for the use of autoclaves. Autoclaving is a process used to destroy microorganisms and decontaminate .
{plog:ftitle_list}
The AMSCO Evolution Medium Steam Sterilizer unique chamber shape promotes even pressure and heat distribution within the medium autoclave. The fully jacketed chamber optimizes even heating and minimizes condensation .
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a . A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.
Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum. It serves as a gasket between the acetabulum and head of the femur, creating a vacuum seal and providing stability between the bones. Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
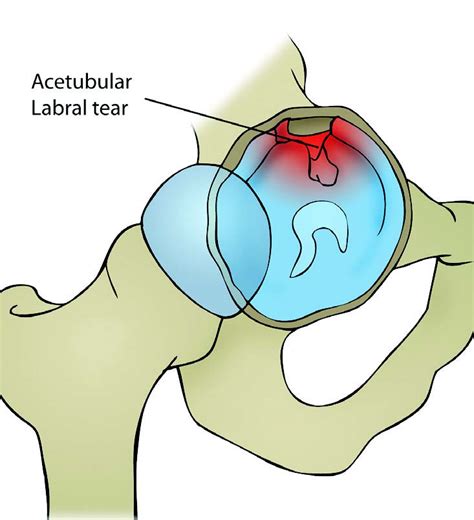
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging. A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket. Specific provocative tests for acetabular labral tears have been described in the literature, all of which involve stressing or loading the hip joint in rotation. However, no single test has been identified as having a significant positive predictive value in . A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.
The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.The hip labrum (also known as the acetabular labrum) is a ring of tough fibrocartilage that covers the rim of the acetabulum. It serves as a gasket between the acetabulum and head of the femur, creating a vacuum seal and providing stability between the bones.
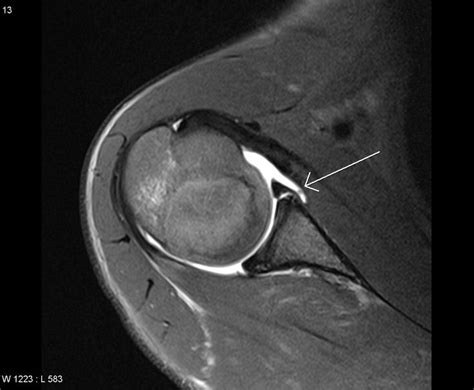
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
right superior acetabular labral tear
labral tear mri images
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging.
A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
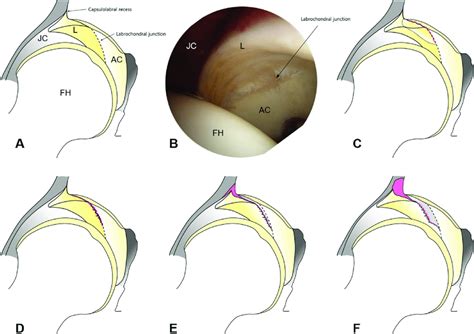
grades of hip labral tears
best imaging for labral tear
ZERIMAR MEDICAL specializes in the repair, maintenance and testing of certain kinds of capital medical and healthcare equipment. That includes things like autoclaves (tabletop and floor .
acetabular labral tear tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology